Genomics Enterprise Center

Genomics Enterprise Center
- RIT/
- College of Science/
- About/
- Facilities/
- Genomics Enterprise Center
The Genomics Enterprise Center at Rochester Institute of Technology employs state-of-the-art genomics technology to produce high-quality data swiftly and affordably.
The Genomics Enterprise Center at Rochester Institute of Technology provides advanced genomics services and resources for faculty, staff, and students. With state-of-the-art equipment and inclusive collaboration, we support a diverse range of research projects. Our dedicated team provides comprehensive training and support services to push the boundaries of genomics. We also welcome external researchers to utilize our world-class facilities and expertise. Let's make groundbreaking discoveries together!
Services and Instrumentation
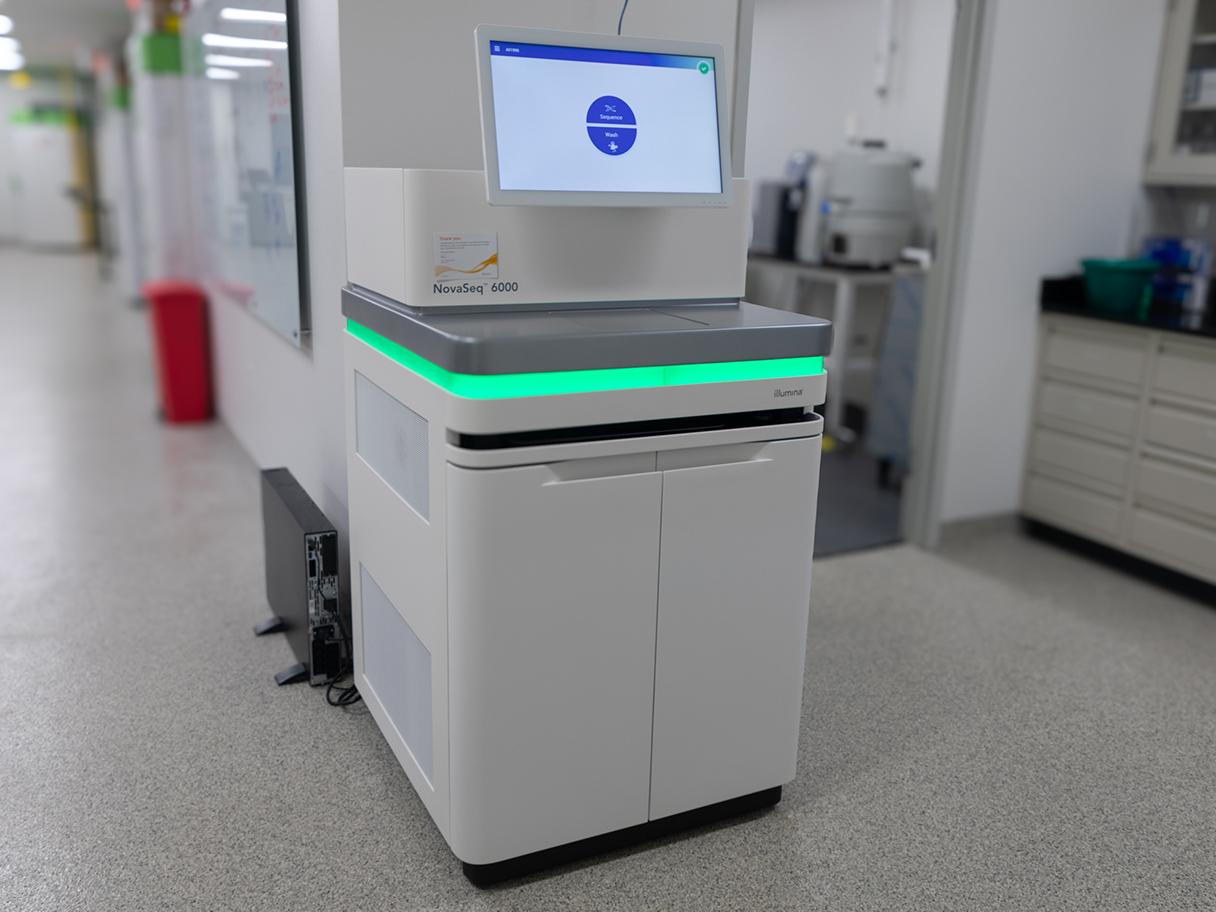
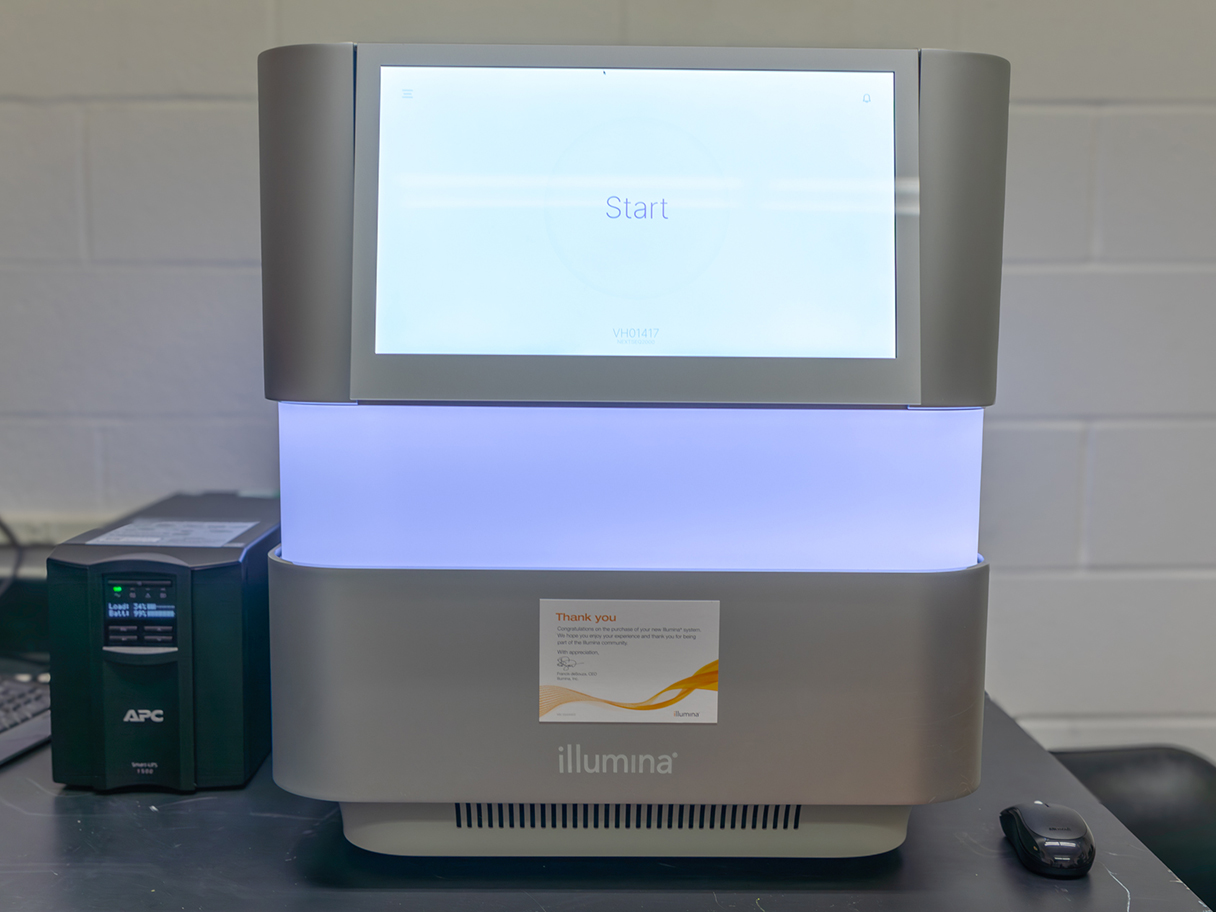
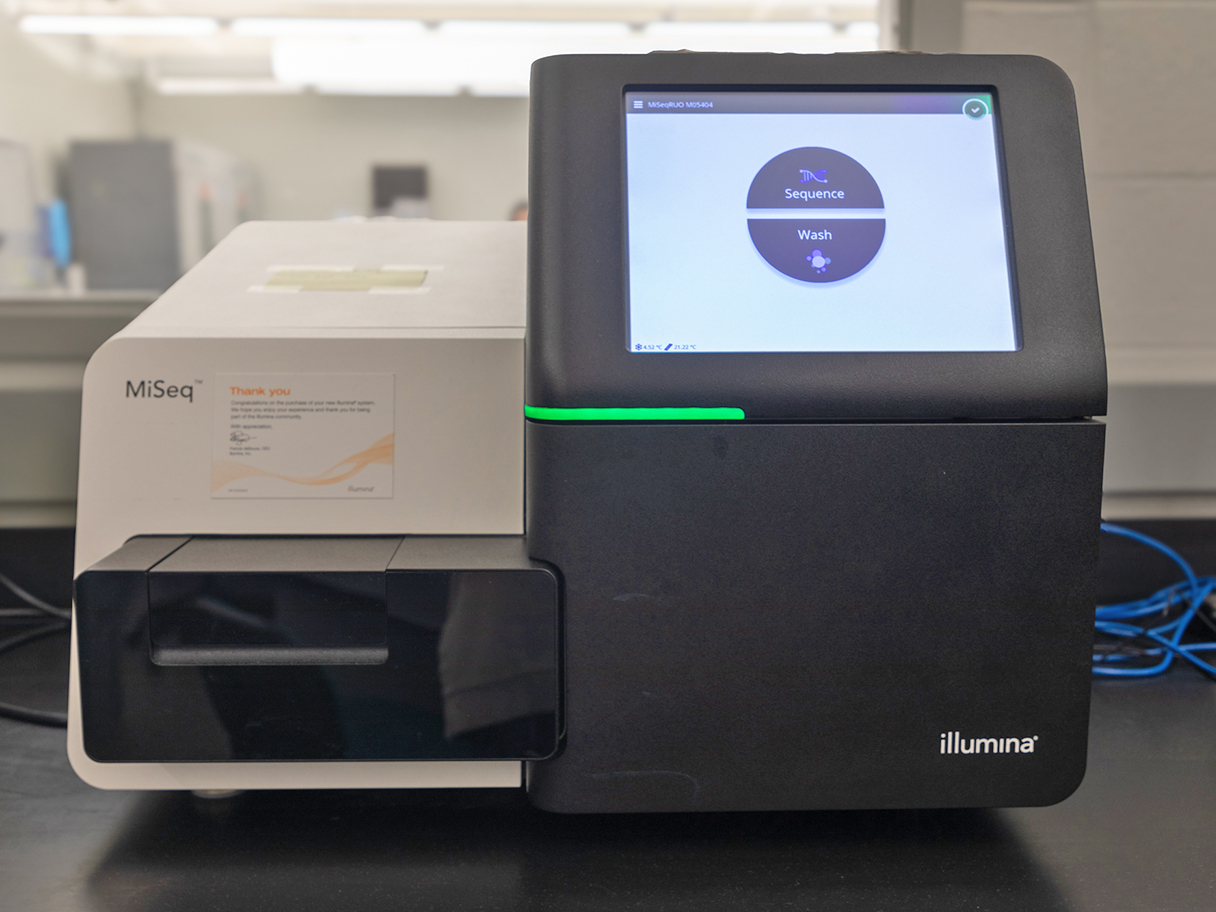
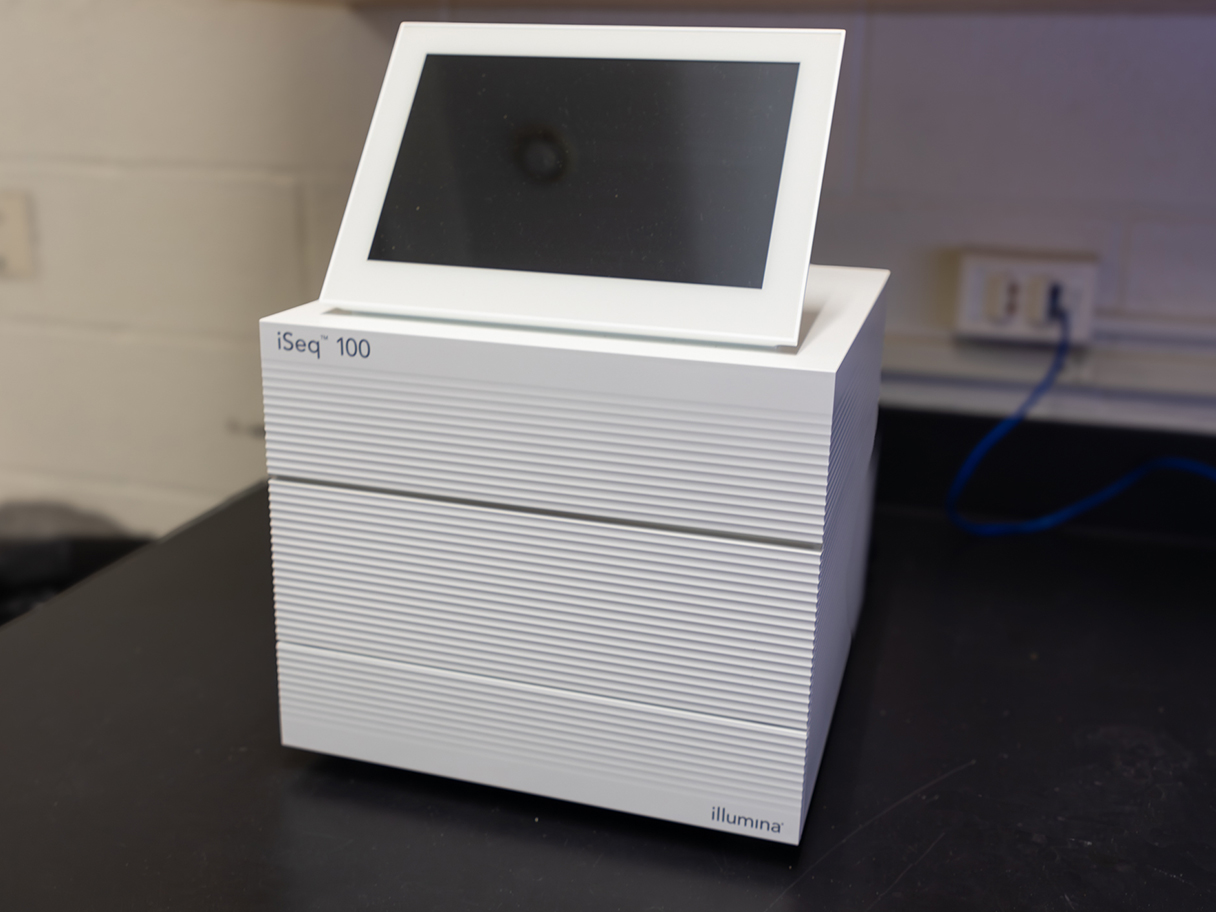
Our comprehensive services cover Illumina next-generation sequencing and Oxford Nanopore Sequencing. Our laboratory is equipped with Illumina's NovaSeq6000, NextSeq2000, MiSeq, iSeq100, and the Oxford Nanopore MinION. We specialize in library preparation and normalization for RNA-seq, DNA-seq, and whole-genome sequencing. Additionally, we offer DNA/RNA quality control using Qubit, Agilent Technologies Bioanalyzer, and Tapestation systems.
Sample Submission Guidelines
The client must complete a Mandate Sample Submission form provided by the Genomics Enterprise Center. The sample can be delivered in person or shipped to the following address:
Genomics Enterprise Center
Rochester Institute of Technology
Thomas H. Gosnell School of Life Sciences (GOS 1263)
Rochester, NY 14623
USA
Minimum: 100ng of high molecular weight genomic DNA in 50 μl buffer (EB or low TE preferred).
Preferred:2μg of high molecular weight genomic DNA in 100 μl buffer. More is always better.
For Small Numbers of Samples (1-16):
Genomic DNA should be electrophoresed to ensure that the sample is high molecular weight (greater than 10kb in length), and the gel image should be provided to the Genomics Enterprise Center upon submission of the sample. The genomic DNA sample should also have been subjected to Nanodrop spectrophotometry to determine sample concentration and purity. The 260/280 ratio should be close to 1.8, and the 260/230 ratio should be close to 2.0. Nanodrop data concerning sample concentration and purity should be provided to the Center upon submission of the sample. The genomic DNA sample should be resuspended in an appropriate buffer such as TE, Qiagen EB buffer, and water. The volume and identity of the buffer should be provided to the Center upon submission of the sample.
For Large Numbers of Samples (17 and more):
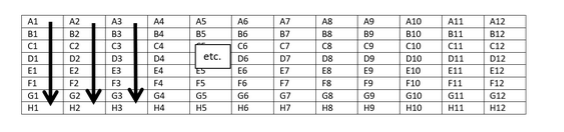
The Genomics Enterprise Center will provide an appropriate 96 well plate for sample submission. The client will array genomic DNA samples in the plate column-wise (i.e., in the order of A1, B1, ..H1, then A2, B2..) and use the well number as the sample number on the Sample Submission Form. At least 20% of the genomic DNA samples should be run out on a gel to ensure that the genomic DNA samples are high molecular weight (greater than 10kb in length). At least 20% of the samples should also be subjected to Nanodrop spectrophotometry to determine sample concentration and purity. The 260/280 ratio should be close to 1.8, and the 260/230 ratio should be close to 2.0. Gel image(s) and Nanodrop data are to be provided to the Center upon submission of the samples. The volume and identity of the buffer should also be provided to the Center upon submission of the samples.
Genomics Enterprise Center Quality Control of DNA Samples
The Genomics Enterprise Center will conduct fluorometric assays (Qubit) to verify sample concentration for each sample. If the samples are not sufficiently concentrated, we may ask the client to submit additional/replacement samples. If the samples are low molecular weight, the client will be asked to provide additional/replacement samples. The Center reserves the right to reject any sample that does not meet internal quality control.
Minimum: 1μg of total RNA in 50ul buffer. Preferred: 4μg of total RNA in 100ul buffer. More is always better. The client may also supply pre-isolated mRNA or Ribominus/RiboZero treated RNA. In both cases, 200 ng of mRNA is required, although more is always better.
For Small Numbers of Samples (1-16):
The RNA sample should be subjected to Nanodrop spectrophotometry to determine sample concentration and purity. The 260/280 and 260/230 ratios should be close to 2.0. Nanodrop data concerning sample concentration and purity should be provided to the Center upon submission of the sample. The total RNA sample should be resuspended in an appropriate buffer such as RNase-free water. The volume and identity of the buffer should be provided to the Center upon submission of the sample.
For Large Numbers of Samples (17 and more):
The Genomics Enterprise Center will provide an appropriate 96 well plate for sample submission. The client will array total RNA samples in the plate column-wise (i.e., in the order of A1, B1, ..H1, then A2, B2..) and use the well number as the sample number on the Sample Submission Form. At least 20% of the samples should also be subjected to Nanodrop spectrophotometry to determine sample concentration and purity. The 260/280 and 260/230 ratios should be close to 2.0. Nanodrop data are to be provided to the Center upon submission of the samples. The volume and identity of the buffer should also be provided to the Center upon submission of the samples.
Quality Control of DNA Samples
The Genomics Enterprise Center will conduct fluorometric assays (Qubit) to verify sample concentration for each sample. The Center will also conduct RNA integrity assays (TapeStation) to determine the integrity of the RNA and determine the RIN value of the samples. If the samples are not sufficiently concentrated, we may ask the client to submit additional/replacement samples. If the samples have low RIN values (an indication of RNA degradation), the Center will ask the client to supply replacement samples if possible. The Center reserves the right to reject any sample that does not meet internal quality control.
Submission of Samples in 96 Well Plate
Submit your samples in the formats shown below in 96 well plate. Start from the left side of the plate and fill-in samples by columns.
Submission Forms
Frequently Asked Questions
Genomics Enterprise Center
Rochester Institute of Technology
Thomas H. Gosnell School of Life Sciences (GOS 1263)
Rochester, NY 14623
USA
Next-generation sequencing, or high-throughput sequencing, refers to a range of advanced technologies, including Illumina Sequencing, Ion Proton semiconductor-based sequencing by Life Technologies, Pacific BioSciences sequencing, Oxford Nanopore sequencing, and various other methods.
The Genomics Enterprise Center at Rochester Institute of Technology is equipped with the following high-throughput sequencing platforms:
- Illumina NovaSeq 6000
- Illumina NextSeq 2000
- Illumina MiSeq
- Illumina iSeq 100
- Oxford Nanopore MinION platform
After the experiment is concluded, the Genomics Enterprise Center stores the remaining samples for up to two weeks.
Contact Dr. Girish Kumar to request a quote or schedule a consultation for a project.
The Qubit 4.0, Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100, or TapeStation 4200 are used to evaluate the quality of DNA and RNA submitted by users. As a precaution, all samples undergo quality assessment by the center before proceeding, regardless of any prior evaluations conducted by users in their own laboratories.
The Genomics Enterprise Center can facilitate experiments using user-prepared libraries. However, users must provide the complete library preparation protocol and precise sequencing specifications. The Center cannot be fully responsible for data quality when portions of the experiment are outside its control. For requirements on pre-made library materials, contact Dr. Girish Kumar.
DNA samples in tubes can be shipped at room temperature for overnight delivery; there's no need to use dry ice or wet ice. However, RNA samples should be shipped on dry ice. Only use courier services (FedEx, UPS, DHL) and send to the following address:
Genomics Enterprise Center
Rochester Institute of Technology
Thomas H. Gosnell School of Life Sciences (GOS 1263)
Rochester, NY 14623
USA
Samples are processed in the order received, on a first-come, first-served basis. Processing time depends on the queue length. For RNA or DNA submissions, results are typically provided within 2 to 4 weeks, but this timeline is not guaranteed. For library or pool submissions, data delivery usually occurs within 1-2 weeks, though this timeline is also not guaranteed.
If you have an upcoming deadline for a paper, grant, or presentation, contact Dr Girish Kumar. We will work closely with you to ensure your project is completed by the desired deadline.
The Genomics Enterprise Center will store submitted samples for two weeks. After that, we will contact you to determine if you want the materials returned or disposed of. If you wish to have your samples returned at any time, contact the Center, and we will be happy to facilitate the return.
The sequencing data will be shared using Globus, a service that facilitates research data management, particularly file transfers. It allows users to transfer files between locations they have access to, using the GridFTP protocol for quick, secure, and reliable data transfers.
“We gratefully acknowledge the technical support from the Genomics Enterprise Center at Rochester Institute of Technology."
Genomics Publications
1. Kumar, G., Gan, H. M., Wengert, P., Penix, T., Parthasarathy, A., Hudson, A. O., & Savka, M. A. (2024). Whole-genome sequencing of four culturable endophytic bacteria from German hardneck garlic cloves (Allium sativum L.). Microbiology Resource Announcements, e01225-23.
2. Kumar, G., Gan, H. M., Popielarz, H., Steele, J., Parthasarathy, A., Hudson, A. O., & Savka, M. A. (2023). Endophytic bacteria associated with wild-type banana seed (Musa balbisiana): whole genome sequencing. Microbiology Resource Announcements, 12(12), e00650-23.
3. Tuytschaevers, S., Aden, L., Greene, Z., Nixon, C., Shaw, W., Hatch, D., ... & Hudson, A. O. (2024). Isolation, whole-genome sequencing, and annotation of two antibiotic-producing and antibiotic-resistant bacteria, Pantoea rodasii RIT 836 and Pseudomonas endophytica RIT 838, collected from the environment. Plos one, 19(2), e0293943.
4. Cavanaugh, N. T., Kumar, G., Reverdy Pearson, A., Colbert, J., Riquelme, C., Hudson, A. O., ... & Godoy, V. (2024). Whole-Genome Sequencing of a Janthinobacterium sp. Isolated from the Patagonian Desert. bioRxiv, 2024-02.
5. Cavanaugh, N. T., Kumar, G., Couto Frignani, M., Thewedros, N., Twahirwa, M., Riquelme, C., ... & Godoy, V. (2024). Whole-Genome Sequencing of Three Extremophile Bacillus subtilis Strains Isolated from the Atacama Desert. bioRxiv, 2024-02.
6. Gan, H. M., Penix, T. S., Wengert, P. C., Wong, N. H., Hudson, A. O., Kumar, G., & Savka, M. A. (2023). Whole-Genome Sequence of Endophytic Bacteria Associated with Poison Ivy Vine (Toxicodendron radicans). Microbiology resource announcements, 12(4), e01232-22.
7. Mozrall, A. R., Miranda, R. R., Kumar, G., Wadsworth, C. B., & Hudson, A. O. (2022). Isolation, Whole-Genome Sequencing, and Annotation of Two Antibiotic-Producing and-Resistant Bacteria, Enterobacter roggenkampii RIT 834 and Acinetobacter pittii RIT 835, from Disposable Masks Collected from the Environment. Microbiology Resource Announcements, 11(10), e00757-22.